CompactDry™ YMR HDx, Rapid Yeast & Mold, 240-pk
- Part Number:
- YMR240 (54084)
- Pack Size:
- 240-pk
- Product Type:
- CompactDry™
- Product Style:
- Yeast and Mold
Description
Usage of Compact Dry YMR is a simple, safe and fast test procedure for determination and quantification of yeasts and molds in foods or raw materials – as well as pharmaceutical raw materials. The incubation time from application of sample/sample dilution to the final evaluation in most food matrices is only 48 hours! For some special food matrices which contain growth reducing substances the incubation time needs to be extended to 72 hours.
The Compact Dry plates in general consist of a special 50 mm diameter petri dish containing a detection specific nutrient pad. The ready-to-use, chromogenic Compact Dry plates are suitable for in-process controls as well as controls of finished products. In conjunction with other products, such as Hardy’s EnviroMax Plus® Environmental Sampling Swabs (Cat. No. 2588050PFB), Compact Dry plates may also be used for surface sampling and therefore applied for quantitative hygiene monitoring even at surfaces which are difficult to reach. Compact Dry YMR is scheduled to be submitted for approval at MicroVal, NordVal and AOAC-RI.
General Information
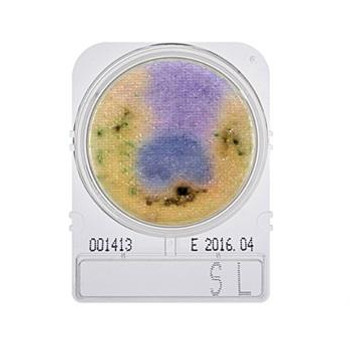
During growth on the nutrient medium of Compact Dry YMR, colonies of yeasts and molds show different color reactions and therefore they are easy to differentiate. The chromogenic substrate X-Phos develop a blue green color with nearly all yeast colonies. Molds will appear quickly as light blue, diffuse looking colonies and later on form their typical three-dimensional structures in the air space between the nutrient pad and plate cover. The coloration of the air structures might be different according to the special type of mold. Growth of bacterial species on Compact Dry YMR is inhibited by antibiotics which are added to the medium.
Yeasts
Yeasts are facultative anaerobe, monocellular fungi (Ascosporidae), fermenting sugar substrate to CO2 and H2O. Under anaerobic conditions yeasts ferment sugar to alcohol and CO2. Those qualities are commercially used in the brewing, wine and baking industry. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the most common strain used for industrial purposes. In terms of food spoilage, genera of Candida play a major role. This germ is located in human and animal mucosa (nose, throat).
Molds
The term “mold“ is commonly used for the visible part of the fungi present on the surface of contaminated food. Under the surface the fungi forms mycelium, which cannot be recognized with the naked eye. Specific molds, as well as yeast, are used for industrial purposes (e.g. cheese production). Harmful genera of molds exist as well and are able to produce toxins (mycotoxins). Almost all molds have an allergenic potential related to their spore forming capabilities. Besides food spoilage, molds are environmental concerns when buildings become infested by molds.